What Is Parotid Tumor Surgery and Who Need It Most
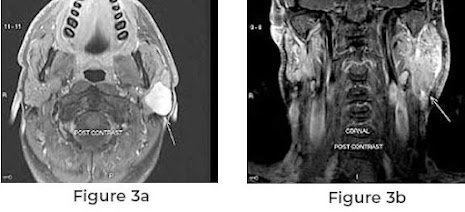
Parotid tumor surgery, also known as parotidectomy, is a surgical procedure performed to remove tumors or growths located in the parotid gland. The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands and is located on either side of the face, just in front of the ears. Tumors in this gland can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). There are several reasons why someone might need parotid tumor surgery. Diagnosis of a Parotid Tumor If a lump or growth is found in the parotid gland, further investigation, including imaging tests and biopsies, may be needed to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Surgery may be recommended as part of the treatment plan. Know About the Symptoms Parotid tumors can cause symptoms such as pain, swelling, difficulty swallowing, or facial weakness. If these symptoms are present and are affecting the patient's quality of life, surgery may be recommended to remove the tumor and alleviate symptoms. Mali


