The Following Are Some Facts Concerning Parotidectomy That People Should Be Aware Of.
The parotid gland, which is the largest and most essential of the salivary glands, is surgically removed in a parotidectomy. The most prevalent reason for the operation is neoplasms (tumors), which are rapidly and incorrectly proliferating cells. Neoplasms can be malignant or benign (noncancerous).
It's worth emphasizing that the parotid tumor surgery choice is based on maintaining the facial nerve in order to avoid significant morbidity (diseases). Furthermore, many doubts remain concerning which procedure to choose and the chances of cancer recurrence.
The parotid glands are removed during a parotidectomy with a facelift incision:
• Because of the type of incision and the reconstructive method employed, patients who undergo a parotidectomy typically notice a difference in their look.
• A facelift incision parotidectomy is a comprehensive operation that combines our head and neck and plastic surgeons' expertise to safely remove parotid gland tumors with minimal scarring. The facial nerve is in charge of closing your eyes, raising your brows, and smiling.
• Your surgeon will do a facelift with an incision that runs behind the ear rather than down the neck, resulting in a more hidden incision. After the tumor is removed, dermal fat grafts (fat retrieved from the abdomen or a muscle flap) are utilized to restore the symmetry of the face, ensuring that your appearance is kept.
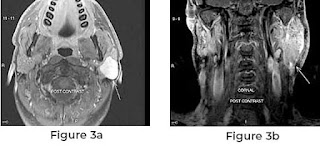
Approaches to parotid tumor surgery have been developed to give a safe procedure, limit nerve morbidity, and provide aesthetic satisfaction. We used a facelift incision to perform two parotidectomy surgeries. One example was rebuilt at the parotid bed using a superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) flap and a sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle rotated flap. In the second patient, the same operations were performed, but a collagen membrane was added to prevent Frey's syndrome. After surgery, two instances obtained beautiful results without the use of a neck scarf and a hollow defect on the parotid bed area.



Comments
Post a Comment